
IL2RG Gene Therapy for X-SCID
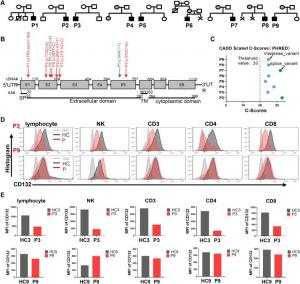
(A) Family pedigrees of the patients. The black solid symbols indicate the affected patients (P1–P9), the grey solid symbols indicate carriers of the same gene mutation, and the open symbols indicate unaffected family members. The squares indicate male su
Pre-clinical validation of SIN-EFS-IL2RG.co vector-based gene therapy for X-SCID
CHINA, March 13, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency disease (X-SCID) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by profound defects in T-cell, B-cell, and natural killer (NK) cell function, caused by mutations in the interleukin-2 receptor γ-chain (IL2RG) gene. Current treatment options that restore immune functions include hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and gene therapy; however, the clinical application of HSCT is limited by the shortage of suitably matched donors. With 300 births per year, China has seen a rising incidence of X-SCID, highlighting the urgent need to develop gene therapy protocols tailored to the Chinese cohort.
In a recent study published in the Genes and Diseases journal, researchers at the Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, Ubrigene (Beijing) Biosciences Co. Ltd, and Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine report a pre-clinical study that evaluates the safety and efficacy of SIN-IL2RG-LV vector-based gene therapy for X-SCID.
Using next-generation screening and Sanger sequencing, the authors identified six novel IL2RG mutations in a Chinese cohort of nine X-SCID patients. Of the nine patients, two adolescent patients with an atypical immunotype were confirmed by analyzing IL-2-JAK-STAT5 signaling, T cell proliferation, and T cell receptor excision circles (Trecs).
Self-inactivating lentiviral vectors (SIN-LV) comprising either the naive/wild-type (IL2RG.wt) or codon-optimized (IL2RG.co) IL2RG cDNA sequences placed under the transcriptional control of an EFS promoter and incorporated with a mutated WPRE∗ were constructed and subsequently transfected into ED7R cells deficient in IL2RG and human BM CD34+ cells. In both cells, the EFS-IL2RG.co vector increased the expression of IL2RG mRNA and CD132 protein compared to the EFS-IL2RG.wt.
Transduction of the EFS-IL2RG.co vector in large-scale cultures of human mobilized CD34+ cells in a GMP workshop increased CD132 protein levels without compromising cell viability or purity. Additionally, in vivo studies showed that SIN-EFS-IL2RG.co vector-transduced CD34+ cells lacked oncogenicity. Finally, the authors demonstrated the successful ex vivo transduction of CD34+ cells from patients with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency disease (X-SCID).
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the safety and efficacy of the SIN-EFS-IL2RG.co vector for gene therapy in X-SCID. Furthermore, the authors affirm its GMP compliance and its potential to facilitate further clinical trials in X-SCID gene therapy in China.
Reference
Title of the original paper - Preclinical ex vivo IL2RG gene therapy using autologous hematopoietic stem cells as an effective and safe treatment for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency disease
Journal - Genes & Diseases
Genes & Diseases is a journal for molecular and translational medicine. The journal primarily focuses on publishing investigations on the molecular bases and experimental therapeutics of human diseases. Publication formats include full length research article, review article, short communication, correspondence, perspectives, commentary, views on news, and research watch.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101445
Funding Information:
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82070135)
The National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFC2700804)
The CQMU Program for Youth Innovation in Future Medicine (China) (No. W0100)
# # # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3 | Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases)
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
email us here
Visit us on social media:
Facebook
X
LinkedIn
Instagram
YouTube
Other
Distribution channels: Education, Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals Industry, Science
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Submit your press release

