Researchers explore the role of of transposable elements in myocarditis
USA, May 22, 2024 /EINPresswire.com/ -- This study explores the role of transposable elements (TEs) in modulating immune responses in cardiomyopathy, using RNA-Seq and single-cell sequencing data from a mouse model of experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Findings reveal significant upregulation of immune genes and specific expression of ERVB7-1.LTR-MM transposon across various immune cells, suggesting TEs' substantial impact on the disease's immune mechanisms.
Regarded historically as genomic parasites, transposable elements (TEs) have now been recognized as significant contributors to cellular identity and function, especially in immune regulation.
Mammalian genomes contain a vast number of TEs The diversity and abundance of these elements impact the structure, function and evolution of the genome. They influence gene regulatory networks by altering transcription factor binding sites and creating new enhancer activities. Increasingly, there is evidence that underscores the crucial role of TEs in various diseases, especially in modulating immunity. However, in the context of myocarditis, there has been a notable lack of focus on the impact of TEs, highlighting a potential research area that could provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms driving this cardiac disease.
In a study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbre.2024.03.001) published in the KeAi journal Reproduction and Breeding, a team of researchers from Hunan Normal University utilized RNA-Seq and single-cell RNA-Seq data to identify key TEs associated with myocarditis.
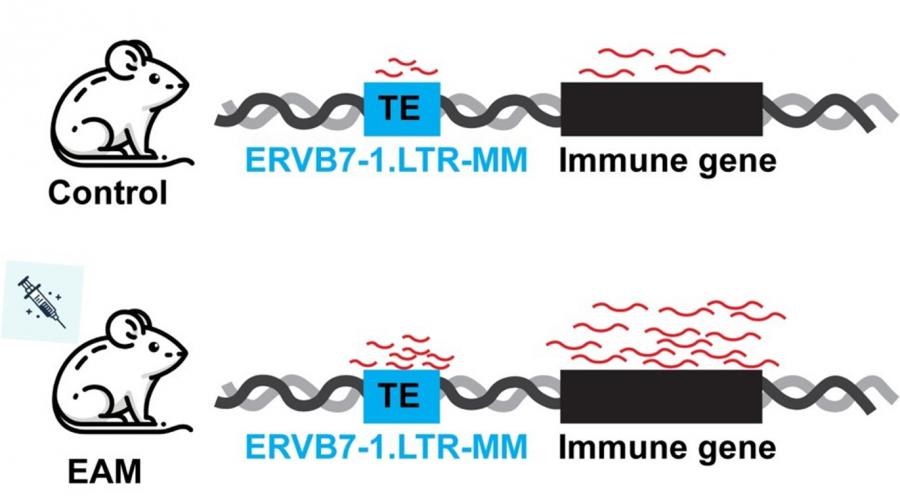
The team used publicly available databases to explore the role of TEs in myocarditis.RNA Seq data and single-cell sequencing data were analyzed, with a focus on the mouse model of experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM). The RNA-Seq analysis revealed substantial upregulation of a range of immune genes in cardiac tissue.
“We furthered the investigation using single-cell sequencing of cardiac immune cells identified specific expression of certain transposable elements (TEs) across different types of immune cells in the heart,” shares first author of the study, Sixing Chen. “We observed an overall increase in the expression of the ERVB7-1.”
LTR-MM transposon across various cells in the EAM model suggest a widespread impact of this transposon on the immune response in this disease context.
“Our findings highlight the intricate interaction between TEs and the immune system in cardiomyopathy, providing new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying this condition,” adds Chen.
In particularly, the discovery of specific TEs expression in cardiac immune cells and the overall increase in ERVB7-1. LTR-MM expression across the EAM model underscore the potential of these elements in modulating immune responses and contribute to our understanding of cardiomyopathy's pathogenesis. These observations open avenues for further research into the role of TEs in cardiac diseases, optimizing novel therapeutic strategies.
DOI
10.1016/j.repbre.2024.03.001
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbre.2024.03.001
Funding information
The present study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos: 31872315, 81970324, 81700338, 81800289, 81670290);the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2023JJ30396) and Key Projects of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (No.23A0082).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
EIN Presswire does not exercise editorial control over third-party content provided, uploaded, published, or distributed by users of EIN Presswire. We are a distributor, not a publisher, of 3rd party content. Such content may contain the views, opinions, statements, offers, and other material of the respective users, suppliers, participants, or authors.